What is Ethernet?
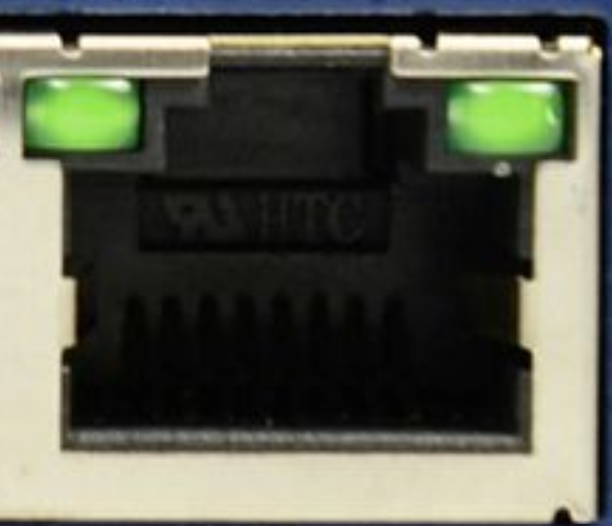
Ethernet is a common networking technology that uses cables to connect devices to local area networks (LANs). The Ethernet port, also known as an RJ45 port, allows wired internet and network access.
What Is It Used For?
- Connecting computers, printers, or other devices to a router or modem
- Providing stable and fast internet connections
- Supporting large file transfers or streaming with minimal latency
- Creating secure and reliable local networks in homes or offices
Common Misunderstandings
- Ethernet is not obsolete. It is often faster and more stable than Wi-Fi
- Not all Ethernet cables are the same. Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat7 have different speed and shielding capabilities
- An Ethernet port is larger than a phone line port, even though they look similar
- Plugging into an Ethernet port does not automatically mean internet access. The network must be active
How to Identify It
- Rectangular port slightly wider than a USB port
- Often found on the sides of laptops or the backs of desktops and routers
- Usually labeled as "LAN" or shows a symbol of connected squares
- Has a small tab inside that clicks when the cable is inserted
Devices That Commonly Use Ethernet
- Desktop computers — connect to wired networks for stable internet access
- Laptops — often include Ethernet ports or use adapters for reliable connectivity
- Routers — distribute internet access through Ethernet ports
- Modems — connect to ISPs and deliver internet via Ethernet
- Network switches — manage traffic between multiple Ethernet-connected devices
- Servers — rely on Ethernet for fast and secure data transfer
- Smart TVs — use Ethernet for uninterrupted streaming and updates
- Game consoles — connect via Ethernet for low-latency online gaming
- Printers — use Ethernet to connect to office or home networks
- IP cameras — rely on Ethernet for both power (via PoE) and video transmission